THE KNEE JOINT
Joints are the areas where bones meet, and movement occurs. The knee joint is made up of the femur above and the tibia below. The two bones are separated by cartilage that acts as a cushion and allows movement.
REASONS FOR SURGERY
The reasons for total knee replacement surgery in Delhi are: severe pain, loss of mobility, or deformity of the knee. Symptoms may be due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or trauma among others.
Osteoarthritis, commonly called “wear and tear,” is the most common cause for a total knee replacement.
ABOUT KNEE REPLACEMENT
The knee joint is made up of the ends of the thigh bone (femur) and the shin bone (tibia). These bones normally slide over each other with ease because they are covered by soft cartilage. If an injury damages the cartilage or is worn away by arthritis, for example, it can make the joint ache or stiff.
Generally, a new knee joint improves mobility and decreases pain, although your new knee will not be able to bend as much as a normal knee joint.
Depending on the condition of your knee joint, they will replace part or all of your knee joint. A total knee replacement is more common.
Artificial knee pieces can be made of metal and / or plastic, and a knee replacement can last up to 20 years.
WHAT ARE THE ALTERNATIVES?
Knee replacement surgery in Delhi is generally recommended only if nonsurgical treatments, such as physical therapy and exercise, taking medication, or using physical support devices such as a cane, no longer help decrease pain or improve mobility.
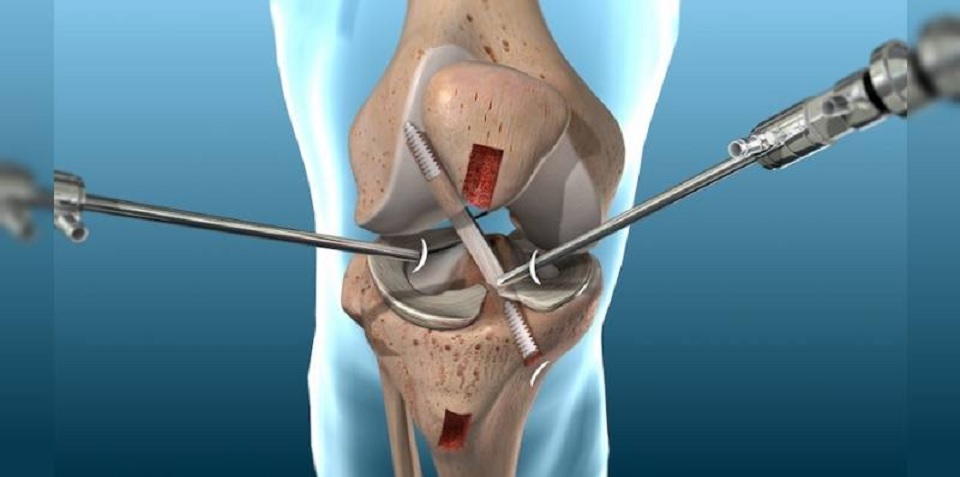
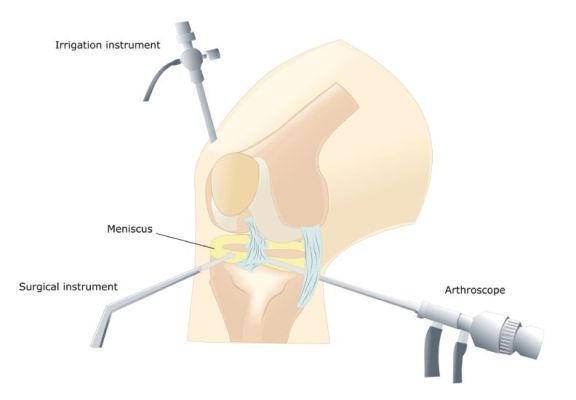
Alternative surgical procedures include arthroscopy in Delhi (if the arthritis is not very severe) or osteotomy (in which the leg bones are cut and put back). You may have already had these procedures before your knee replacement.
The surgeon will explain your options.
PREPARING FOR A KNEE REPLACEMENT
The orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi will explain how to prepare for the operation. For example, if you smoke, they will ask you to stop smoking, as this increases your risk of chest and wound infection, which can delay your recovery.
Typically, you must stay in the hospital for about five days, and the surgery is performed under general anesthesia. This means that you will be asleep during the operation. Otherwise, if you prefer, the surgery can be performed under epidural or spinal anesthesia. This type of anesthesia completely numbs from the waist down, and you will remain awake during the operation.
If you are going to have general anesthesia, you will be asked to fast. This means that you should not eat or drink, normally, for about six hours before general anesthesia. However, it is important to follow the instructions of your anesthetist.
In the hospital, the nurse can check your heart rate and blood pressure and do a urine test.
Your surgeon will explain to you what will happen before, during, and after the procedure, and any pain you may have. This is your opportunity to understand what will happen, and it may be helpful to prepare questions about the risks, benefits, and other alternatives to the procedure. This will help you stay informed so that you can give your consent if you are asked to sign a consent form to carry out the procedure.
You may be asked to wear compression stockings on your unaffected leg to prevent blood clots from forming in your veins (deep vein thrombosis, DVT). You may need an injection of a blood-thinning medicine called heparin in addition to, or instead of wearing, compression stockings.
WHAT HAPPENS DURING A KNEE REPLACEMENT?
Generally, a knee replacement in Delhi takes about two hours.
The orthopaedic in Delhi will make a single cut (10 to 30 cm long) in the front of your knee. You will push the kneecap to the side to reach the knee joint. The surgeon will remove the worn or damaged surfaces from the end of the femur and the top of the tibia. Typically, he will remove the anterior cruciate ligament and may remove the posterior cruciate ligament. For support, the best orthopaedic in Dwarka will not remove the collateral ligaments. It will shape the surfaces of the femur and tibia to fit the artificial knee joint and then fit the new joint over both bones.
Sometimes the back of the kneecap is replaced with a piece of plastic. This is known as patella lining.
After placing the new joint, the surgeon will close the wound with stitches or clips and cover it with a bandage. The surgeon will place a tight bandage on your knee to help minimize swelling.
WHAT SHOULD I EXPECT AFTER

You will need to rest until the anesthesia wears off. After epidural anesthesia, you may not be able to feel or move your legs for several hours.
You may need pain relievers to ease any discomfort when the anesthesia wears off.
You may have an intermittent compression pump attached to special pads on your lower legs for the first day or so. By inflating the cushions, the pump encourages healthy blood circulation and helps prevent a DVT. You can also have a compression stocking on your unaffected leg. This helps maintain circulation.
A physiotherapist in Dwarka (a movement and mobility specialist) will visit you daily to guide you through exercises that will help you recover.
You will stay in the hospital until you can walk safely with the help of a cane or crutch. When you can go home, you will need to ask someone to drive you.
Before you go home, the nurse will give you recommendations for caring for your knee and a date for your follow-up appointment.
How long it takes for the sutures to disappear will depend on the type used in the surgery. However, for this procedure they usually go away in about six weeks. Nonabsorbable sutures and clips are removed 10-14 days after surgery.
RECOVERING FROM KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY
If necessary, you can take an over-the-counter pain reliever, for example acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Follow the instructions in the patient information leaflet that comes with your medicine, and if you have questions, ask your pharmacist.
Physical therapy exercises are an indispensable part of your recovery, so it is essential that you continue to do them for at least two months.
You will be able to move around your house and go up and down stairs. For a few weeks, some everyday activities, such as shopping, will be difficult for you to do. You may need to use a cane or crutches for about six weeks.
You may be asked to wear compression stockings at home for several weeks.
When resting, raise your leg and support your knee to help prevent leg and ankle swelling.
Depending on the type of work you do, you may be able to go back to work after six to 12 weeks.
Follow your surgeon’s recommendations for driving. You should not drive until you are sure that you can brake in an emergency without discomfort.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS?
Knee replacement surgery in West Delhi is a common and generally safe procedure. However, in order to make an informed decision and consent, you must be aware of the possible side effects and risk of complications associated with this procedure.
Side effects
These are the unwanted, though mostly temporary, effects of successful treatment; for example, feeling dizzy as a result of general anesthesia.
Your knee will hurt and be swollen for up to six months.
You will have a scar on the front of your knee. You may not have sensation in the skin around the scar. This may be permanent, but it should get better in two years.
Complications
Complications are problems that occur during or after the operation. Most of the people are not affected. Possible complications from any operation include unexpected reactions to anesthesia, excessive bleeding, or clot formation, usually in a vein in the leg (DVT).
Complications specific to knee replacement are rare, but include:
- Wound or joint infection Antibiotics are given during and after surgery to prevent this complication.
- Unstable joint. The knee joint may loosen and may require surgery to correct it.
- Damage to blood vessels or nerves. It is usually mild and temporary.
- Scar tissue. Scar tissue formation can limit movement. You will likely need another surgery to correct it.