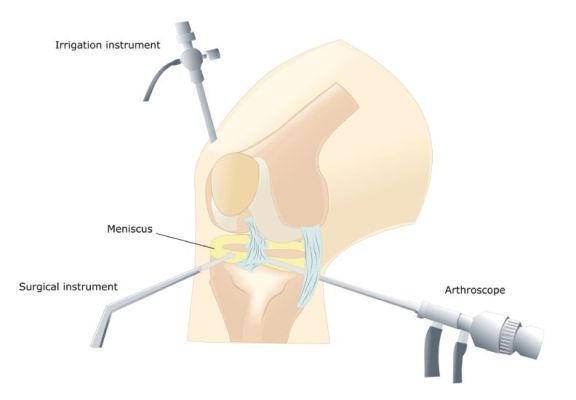
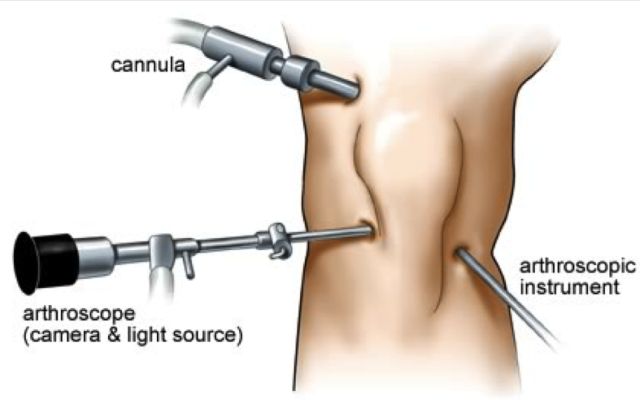
What is knee arthroscopy?
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows access and treatment of injuries that affect the various structures of said joint. For this, 2 or 3 small incisions of less than one centimeter are made that allow access to the joint.
Most knee surgeries that do not involve the placement of a prosthesis are performed with a complete or partial approach with knee arthroscopy in Delhi. It is the technique of choice to address many injuries because it allows a better and greater visualization of the joint. In a non-aggressive way, all the points of the knee can be accessed to clean the cartilage, small perforations of the bone that lacks cartilage (microfractures), stabilize the cartilage and apply substances or elements that allow the cartilage to regenerate (plasma rich in platelets or stem cells).
Likewise, knee arthroscopy is also used as support for other open techniques, since it improves the diagnosis and prognosis of the patient’s injury, as it is less aggressive.
The arthroscopy in Delhi can be performed under local, regional or general anesthesia, depending on the injury and the patient. The anaesthesiologist will decide the best method for the patient, as long as he suffers as little as possible.
Why is it done?
Knee arthroscopy is used to solve knee injuries. Thus, meniscus injuries are one of the most common pathologies and, thanks to arthroscopy, it is possible to preserve most of the menisci, since the resection is not complete but partial. Meniscal sutures and the possibility of transplanting the meniscus with knee arthroscopy are common techniques that allow better protection of the cartilage of the joint.
Another of the most dangerous injuries related to sports practice is the rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament. If this is injured, it causes instability in the knee that makes it impossible for the patient to perform practically any sport. If the instability continues, it can damage surrounding structures, such as the menisci and cartilage. Hence, it is necessary to reconstruct the anterior cruciate ligament with grafts, accessing the joint through arthroscopy.
On the other hand, cartilage injuries (chondroplasties, osteoarthritis or osteochondritis) are also very common. Preserving the cartilage will also preserve the joint, avoiding wear and tear on the knee.
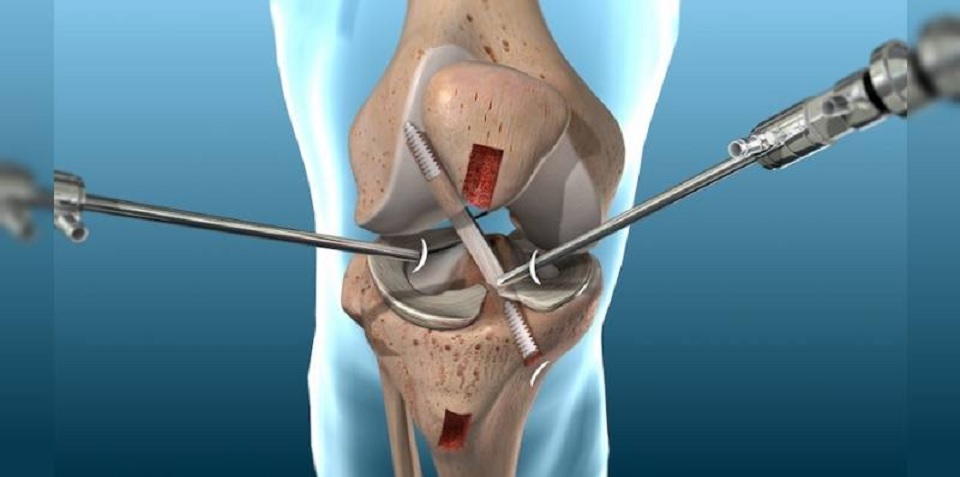
What does it consist of?
The orthopaedic in Delhi will make the small incisions in the knee to be able to access it. He will first fill the knee joint with a sterile solution and remove any cloudy fluid. This way he will be able to see the joint clearly and in detail.
The orthopaedic in Dwarka will then insert the arthroscope (a very thin device with a camera on the end) into the knee. This device sends the images to the television monitor, so that the surgeon can see all the structures in detail. Through the other holes, the surgeon will introduce the surgical material that will allow him to address the injury and repair the damaged structures.
It is a procedure that usually does not last more than an hour. After that, the patient will be transferred to a rehabilitation room and will be able to leave the hospital after two hours, more or less.
Preparation for knee arthroscopy
Before surgery, the patient must undergo a complete physical examination so that the specialist can assess their health and any anomaly that may interfere with the arthroscopy. Likewise, the patient must inform the orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi of the medication he takes, so that he can tell him which ones he should stop taking before the intervention. Some complementary preoperative tests will also be carried out, such as magnetic resonance imaging, electrocardiogram or blood tests.
Care after the intervention
Recovery after arthroscopy is faster than conventional open surgery. However, the advice of the specialist must be followed so that the knee recovers correctly.
It is normal for the patient to experience swelling in the days after the intervention, so it is recommended that the leg be elevated during those first days after the surgery. Also, the application of ice will relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
The incisions should also be healed, keeping them clean and dry. The orthopaedic in West Delhi will tell the patient when they can shower or change the bandage.
On the other hand, shortly after the intervention, the patient must begin rehabilitation exercises with a Physiotherapist in Dwarka, who will establish a program appropriate to the patient and the injury. This will help restore motion and strengthen your knee muscles.
Alternatives to this treatment
The alternative to knee arthroscopy in West Delhi will be conventional open surgery, which is currently only used in more serious cases, in which a prosthesis must be placed. Any other technique will suppose a greater invasion in the knee and a worse postoperative period.